No products in the cart.
October 8, 2024 8:39 am
October 8, 2024 8:39 am
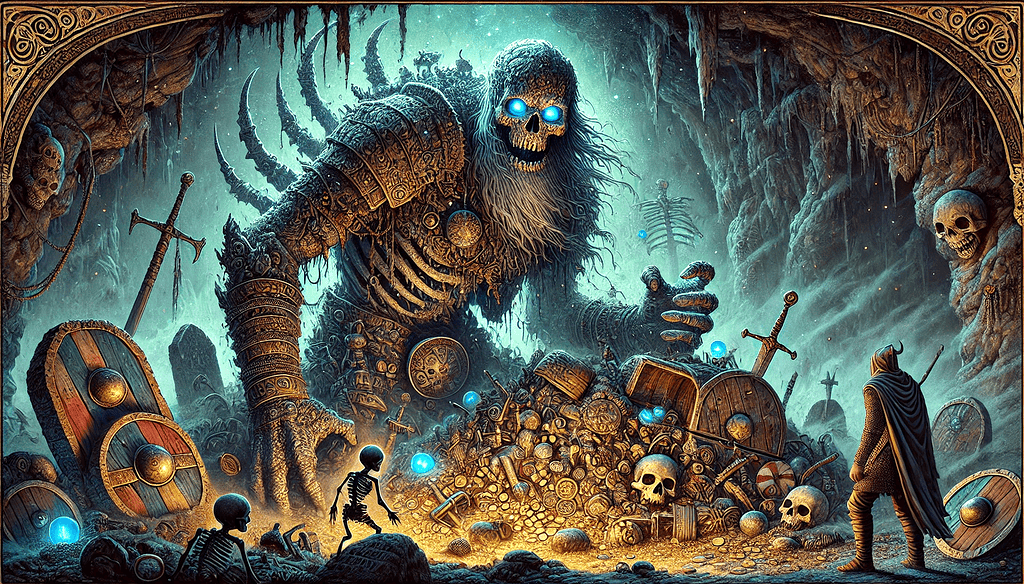
In Norse mythology, draugr are fascinating undead beings known for their eerie presence and formidable powers.
These beings play a crucial role in Icelandic and Scandinavian culture, representing not only the fears of death but also the belief in life after death and the importance of burial practices.
When studying the historical material on the undead draugr (‘revenant’), particularly the Icelandic sagas and sources, these beings express very complex notions of the afterlife, of the dead and how the dead may communicate with the living before and after Christianization in both Iceland and Scandinavia (Lori Jones et al, 2022, p.9).
This article delves into the world of draugr, exploring their characteristics, origins, and cultural significance. You will discover:
Get ready to explore Viking legends and uncover the secrets of the draug!

The term draugr comes from Old Norse, meaning “rider” or “one who walks after death.” These undead beings are unique; they have both physical and supernatural traits that make them different from other creatures like zombies, ghosts or vampires.
Draugar hold significant importance in Scandinavian folklore. They are believed to be manifestations of individuals who did not find peace in death, often due to unresolved issues or improper burial practices.
According to the American Professor John Lindow who is well known for his research and academic work regarding Old Norse literature, the draugar are deemed as dangerous as they did not receive proper mortuary ritual after passing over to the Other side.
They are ‘Dead without status’ and can not find peace in the afterlife; therefore, they can pose significant distress and problems to the living.
This we learn in particular from the well known draugr Glámr in the Grettis saga (John Lindow, 2022, p. 51).
This connection to ancestral legacy makes them central figures in tales that explore themes of vengeance, protection, and the afterlife.
In addition to ideas regarding how the living may become a draugr after physical death, there appears to be a strong connection between the concept of a draugr and ancestor worship among the pre-Christian Norse people (Laidoner, 2020).
In sagas and legends, draugar serve not only as frightening figures but also as reminders of societal values surrounding death and honor.
Their presence in folklore often reflects communal beliefs about life after death and the consequences of one’s actions during their lifetime.
Understanding draugar provides insight into Viking culture’s complex relationship with mortality. They symbolize fears surrounding death while also representing the enduring nature of human connections even beyond the grave.
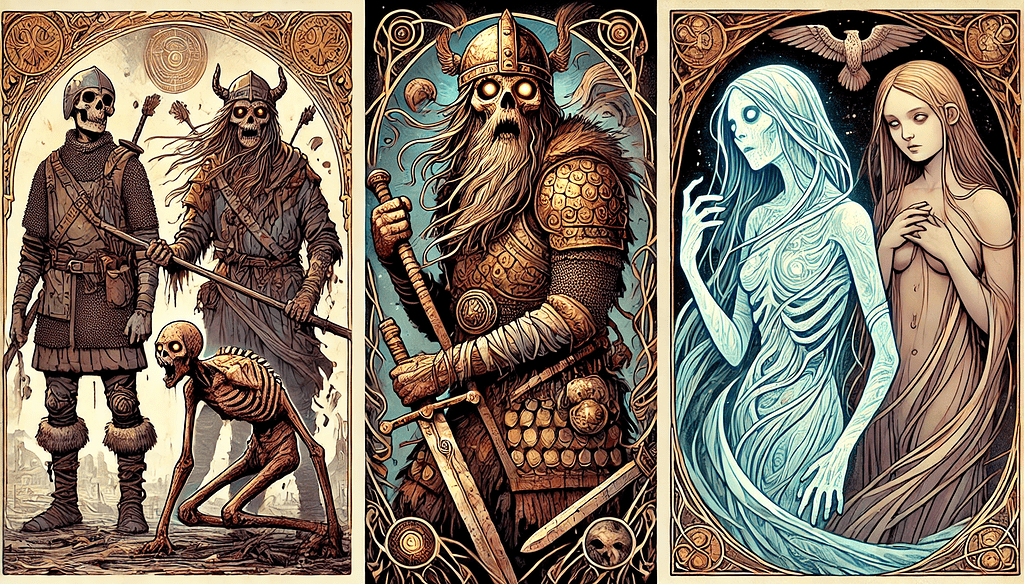
Draugar have unique physical features that make them powerful undead beings in Norse mythology. Their appearance often instills fear and is defined by:
The size of a draugr is particularly noteworthy. Many tales depict these entities as being massive, sometimes compared to an ox or even a great flayed bull.
Such descriptions underscore their intimidating presence and strength, making them feared guardians of burial mounds and treasures.
The symbolism tied to their decaying bodies extends beyond mere horror. Draugar embody the consequences of unresolved life issues and the importance of proper burial practices. Their grotesque appearance reflects the Vikings’ beliefs about death and the afterlife:
In the Laxdaela Saga, encounters with draugar illustrate the havoc they can wreak on the living, reinforcing societal norms regarding death rituals.
As mentioned previously, draugar are ‘the dead without status’ in the afterlife; they have not received proper burial rituals and are therefore capable of reanimating, haunting the living despite being bound to the realm of the dead.
Understanding their physical characteristics reveals how deeply entwined draugar are with Viking culture and beliefs about mortality.

The transformation into a draugr is steeped in the eerie lore of Norse mythology. Understanding this process unveils the complexities surrounding these living dead entities.
Several pathways can lead to becoming a draugr:
Central to understanding draugar is the term aptrgangr, which literally translates to “one who walks after death.”
This notion implies that once a person dies under specific circumstances, they are at risk of returning in this grotesque form. This return signifies more than mere existence; it embodies unfinished business and unresolved conflicts from their mortal life.
The aptrgangr serves as a reminder that not all souls find peace upon crossing the threshold of death.
Viking burial customs played a critical role in preventing the rise of draugar. Protective measures included:
These practices reflect the belief that improper treatment of the deceased could lead to their return as swollen and monstrous figures, often described as being the size of an ox.
Such precautions highlight how deeply intertwined beliefs about death and undead beings were in pre-Christian Norse Scandinavian culture.
Each measure taken was rooted in respect for both life and what lay beyond it, ensuring that those who passed would not become draugar wandering along the road to Hel.
Draugar are not just ordinary undead beings; they possess formidable superhuman strength and a range of magical abilities that set them apart from other entities in Norse mythology.
Their powers often reflect the fears and beliefs of Viking society, embodying both the fear of death and the unknown.
The capabilities of draugar are quite complex. As mentioned they are able to reanimate themselves and rise from the grave. In so far, their powers can be – as mentioned by several scholars in Norse religion and history – quite similar to that of shamans, witches and ritual specialists.
Draugar can shapeshift, are able to see into the future, they can predict the weather.
They possess extreme amounts of physical strength, hence their powers have been sought after and even called upon in order to benefit from their supernatural strength and to defeat an enemy (Hilda Ellis Davidson, 1943, pp. 163, 164).
One famous tale involves a draugr named Grettir’s Saga, where the protagonist Grettir faces off against a powerful draugr that haunts a burial mound.
This creature not only possesses immense strength but also employs magic to attack Grettir with supernatural ferocity.
In another story, Hervarar Saga, a draugr demonstrates its shape-shifting abilities by taking on various forms to mislead its enemies, showcasing how these supernatural traits enhance their menace.
Draugar’s powers significantly impact their interactions with humans. Their ability to control weather can lead to treacherous conditions for those who dare approach their burial sites.
Additionally, their haunting nature underscores the connection between life and death, serving as a reminder of the respect Vikings held for their dead.
The presence of draugar in Viking lore illustrates not only the physical challenges posed by these undead warriors but also emphasizes deeper themes regarding mortality and the afterlife within Norse culture.

Norse sagas provide rich narratives featuring draugar, illustrating their formidable presence in Viking culture. Two notable stories include the Eyrbyggja Saga and the Grettis Saga, both showcasing encounters that reveal cultural lessons and moral implications.
This saga tells of a powerful draugr named Glámr, who haunts the land after death. Glámr’s presence brings misfortune, leading to a series of events that culminate in his eventual defeat. His character represents the fear of the undead as a reflection of unresolved conflicts and societal issues.
Central to this saga is the hero Grettir Ásmundarson, who confronts the draugr Kár. Kár’s supernatural strength poses significant challenges, emphasizing the struggle between human resilience and malevolent forces.
Grettir’s ultimate victory serves as a testament to bravery and cunning in overcoming evil.
These sagas highlight several important themes:
Through these narratives, readers gain insight into how Vikings understood life, death, and the supernatural forces that could disrupt their world.
The draugar serve not only as terrifying figures but also as catalysts for personal growth and moral reflection among the living.
Viking culture held deep beliefs surrounding death and the afterlife, wherein draugar played a significant role. Understanding these undead beings sheds light on Viking practices and their view of mortality.
Burial mounds were not mere resting places; they served as protective sites against draugar. Vikings believed that the dead could rise as these malevolent beings if proper care was not taken during burial. Key aspects include:
The Vikings possessed a rich tapestry of beliefs regarding death:
The cultural significance of draugar extends beyond mere folklore; they encapsulate the fears and reverence Vikings held toward death.
The interplay between burial practices and beliefs surrounding these undead entities reveals much about Viking values related to legacy, honor, and respect for those who have passed on.
Delving into this rich mythology informs our understanding of not just draugar but also the profound complexities surrounding life and death in Viking society.
Draugar have found a captivating place in modern media, especially within video games and literature. Their portrayal often emphasizes their eerie essence and ties back to their roots in Norse mythology.
In Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim, draugar are integral enemies encountered throughout the game. These undead warriors guard ancient tombs, showcasing their warrior past and serving as protectors of treasures.
Players experience intense battles against draugar, which are depicted with notable features:
Their representation extends beyond mere adversaries. Draugar embody themes of death, resurrection, and the consequences of one’s life choices—an echo of their mythological significance.
Contemporary authors have also drawn inspiration from draugar, often using them as symbols of unresolved pasts or moral dilemmas. They appear in various forms across fantasy novels that explore themes of heroism and the supernatural.
In movies and television shows focusing on Viking themes or fantasy settings, draugar sometimes serve as cautionary tales about the importance of proper burial rites.
Their menacing presence reinforces cultural beliefs regarding death and the afterlife.
Draugar continue to resonate in pop culture for their rich lore and haunting imagery.
The blend of horror elements with historical significance captivates audiences, ensuring that these undead warriors remain a compelling subject in storytelling today.
The fear of becoming a draugr haunted the living in Norse culture. The undead warriors were not only feared for their malevolence but also for their potential to rise from the grave and wreak havoc on the living.
To combat this terrifying possibility, various traditional methods were employed during burial practices.
This peculiar method involved binding the deceased’s toes together. The belief was that it would prevent them from walking or rising as a draugr. A body with tied toes would be less capable of moving, thus reducing the chance of them returning to haunt their loved ones.
Another effective measure included placing iron scissors or other iron implements at the grave site. Iron was believed to ward off evil spirits and supernatural beings, including draugar.
The presence of these objects was thought to create a barrier between the dead and the realm of the living.
These practices highlight a deep-rooted concern about death and the afterlife within Viking society. Such rituals served not only as protective measures but also as ways to provide peace of mind for grieving families.
The fear of draugar reflects broader themes in Norse mythology concerning death, honor, and legacy. These traditions emphasize respect for the deceased while illustrating how beliefs surrounding death shaped everyday life in Viking culture.
By understanding these preventive measures, you gain insight into how ancient Norse people viewed life after death and their desire to protect themselves from lingering spirits.
This knowledge provides a richer context for appreciating the complexities of Viking beliefs and their narratives that continue to resonate today.
The question “are draugr evil?” opens a complex dialogue about morality in Norse mythology. These undead beings often embody the fears and concerns of Viking culture, yet labeling them as purely malevolent may oversimplify their role within the mythos.
Draugar are known for their aggressive behavior towards the living, often attacking those who trespass on their burial mounds. However, this aggression can be viewed through a different lens.
They protect their graves and treasures, reflecting a strong connection to their past lives. In this sense, their actions might be interpreted as defensive rather than inherently evil.
The concept of good and evil in Norse mythology differs significantly from modern perspectives. Instead of clear binaries, moral ambiguity prevails.
Actions are often judged based on their outcomes and social context rather than an absolute moral code. This complexity allows for a nuanced understanding of draugar’s intentions.
Draugar represent not only a fear of death but also the unresolved issues that linger after one’s passing. Their existence challenges the living to confront mortality and the consequences of unfulfilled desires or revenge from beyond the grave.
In examining draugr within this nuanced framework, you may find that they serve as reflections of human nature—both flawed and fearful—rather than simple embodiments of evil.
Understanding these complexities enriches your appreciation of Norse mythology’s depth and its exploration of life, death, and everything in between.
Norse mythology is full of stories, characters, and lessons. One group of figures that stands out are the draugr.
They are intriguing beings that deserve a closer look. The complexity of draugar not only reflects the beliefs of the Vikings but also our own understanding of life, death, and what comes after.
One way to understand draugar better is by exploring Viking sagas that feature them. These ancient tales provide valuable insights into how the Norse people viewed these creatures and their significance in their culture.
Draugar also had an impact on burial practices and societal attitudes towards death. By studying their influence, we can gain a deeper understanding of how the Vikings approached mortality and the rituals they performed to honor their deceased.
Contemporary literature and media often draw inspiration from these ancient stories, reimagining them for modern audiences.
By examining these adaptations, we can see how draugar continue to resonate with people today and shape our perceptions of death and the afterlife.
Engaging with the legacy of draugar enriches your understanding of Norse mythology and its lasting impact on culture. By embracing these narratives, you connect with a history that continues to inspire art, literature, and personal beliefs today.
The more you learn about these undead warriors, the more you appreciate their role within the broader context of Viking heritage. So grab your favorite book or video game featuring draugar and immerse yourself in this captivating world.
References and further reading:
Laidoner, T. (2020). Ancestor Worship and the Elite in Late Iron Age Scandinavia: A Grave Matter. United Kingdom: Taylor & Francis.
Ellis, H. R., Davidson, H. R. E. (2013). The Road to Hel: A Study of the Conception of the Dead in Old Norse Literature. United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press.
Death and Disease in the Medieval and Early Modern World: Perspectives from Across the Mediterranean and Beyond. (2022). United Kingdom: York Medieval Press.
Kanerva, K. (2022). The dead in dreams: medieval Icelandic conceptions of the unquiet dead. Journal of Medieval History, 48(2), 218–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/03044181.2022.2049514
Kreager, Adele. (2022). Encounters at the Mound in Old Norse Literature: Dialogues between Landscape and Narrative. Scandinavian Studies. 94. 399-430. 10.3368/sca.94.4.0399.
Lindow, John. “Rites of Passage in Scandinavian Legends” Fabula, vol. 19, no. Jahresband, 1978, pp. 40-61. https://doi.org/10.1515/fabl.1978.19.1.40
Lindow, John. “Ritual and Hierarchy in Old Norse Mythology”.RvT 74 (2022) 46-62