No products in the cart.
September 13, 2024 4:55 am
September 13, 2024 4:55 am
Norse mythology is full of contrasts, with light elves (Ljósálfar) and dark elves (Dökkálfar) representing this deep difference.
The dark elves, mysterious and hard to find, play an important role in Norse stories, showing the complex relationship between light and darkness, although monotheistic concepts of good and evil do not always easily apply to them so easily.
Learning about Dökkálfar will give you a better understanding of the rich and magical Norse Scandinavian culture.
These mysterious beings, often linked to darker aspects and secrecy, reveal the intricacies of Norse belief systems. Discover the hidden truths of the Dökkálfar and delve into their fascinating realm within Norse mythology.

Dark elves, or Dökkálfar, are mysterious beings in Norse mythology. Unlike their brighter counterparts, the Ljósálfar or Light Elves, Dökkálfar are often portrayed as elusive and shadowy figures.
They reside in the gloomy realm of Svartálfheim, a world filled with darkness and secrecy. Ancient texts describe them as creatures with a dusky complexion, darker than pitch itself, embodying the very essence of night.
The contrast between Dökkálfar and Ljósálfar highlights the contrast present in Norse legends.
While Light Elves live in Álfheimr—a bright domain filled with beauty and radiance—Dark Elves make Svartálfheim their home, a place that is pitch black as medieval historian and French Professor Claude Lecouteux writes in ‘Encyclopedia of Norse and Germanic Folklore, Mythology, and Magic’ (2016).
This stark difference reflects the broader themes of light versus darkness within the world of Norse stories.
Historical views have not been kind to the Dökkálfar. In various sagas and writings, they are often linked to wickedness and betrayal.
This perspective may be influenced by Christian symbolism, which frequently equates darkness with evil. Yet, within the rich tapestry of Norse mythology, these dark elves also possess unique powers and wisdom.
It is important to note that dualistic concepts of good and evil can not always be easily applied within pre-Christian ‘pagan’ cosmologies such as the Norse.
They embody a complex nature that challenges simplistic moral classifications.
“The Dökkálfar remind us that shadows exist alongside light, each playing a crucial role in the cosmic balance.”
Understanding these intricate beings offers deeper insights into Norse Viking beliefs about good and evil, light and darkness.
The contrast between Dökkálfar and Ljósálfar encapsulates the complex interaction between these opposing forces, reflecting a worldview where both elements are necessary for harmony.
The origins of dark elves, or Dökkálfar, in early Germanic folklore are complex and filled with myths and legends.
These beings are deeply rooted in old Norse poetry and the sagas that have shaped our understanding of Norse mythology, however, with such sources comes also the potential risk of Christian overlays and distortions.
The Dökkálfar are often contrasted with their lighter counterparts, the Ljósálfar, creating a duality that reflects the broader themes of light and darkness within these ancient stories.
In early Germanic folklore, dark elves were mysterious and elusive creatures, often associated with the underground and hidden realms.
They were believed to possess unique powers and abilities that set them apart from other mythological beings. Unlike the more benevolent light elves, Dökkálfar were often linked to darker aspects of nature and human existence.
The portrayal of Dökkálfar was significantly influenced by Christian symbolism as Norse mythology intertwined with Christian beliefs.
With the spread of Christianity across Scandinavia, many pagan symbols and figures were reinterpreted through a Christian lens (see e.g. Hilda Davidson, 1993).
This fusion led to the association of dark elves with evil and malevolence, mirroring the dichotomy between angels and demons found in Christian doctrine.
A crucial source for understanding dark elves is Snorri Sturluson’s Prose Edda. Written in the 13th century, this work provides valuable insights into Norse cosmology and mythology.
In it, Sturluson describes the Dökkálfar as dwelling in Svartalfheim—a realm distinct from Álfheimr, home of the light elves.
Sturluson’s accounts also highlight the roles played by various deities such as Freyr, Thor, and Loki in relation to these mystical beings. For instance:
These stories weave together a rich cultural significance that continues to captivate modern audiences.
The enigmatic nature of Dökkálfar, combined with their intricate connections to gods like Ymir—whose body formed parts of the world—emphasizes their integral role within Norse mythology’s grand narrative.
Understanding these origins enriches our appreciation for Viking culture and its profound influence on contemporary interpretations of mythical beings.
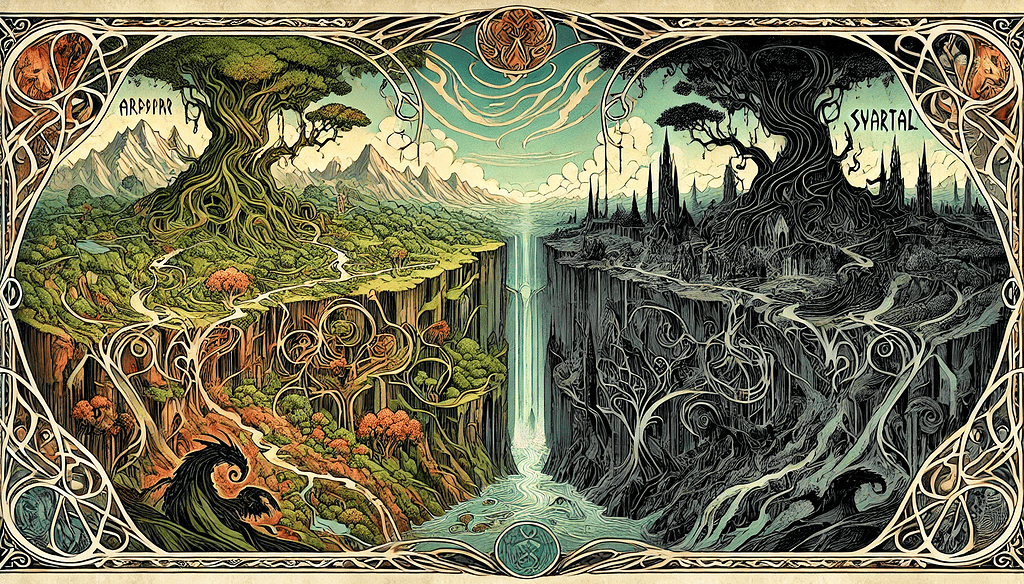
In Norse mythology, Svartalfheim is known as the realm of dark elves. It is a mysterious and dark underground world where these enigmatic beings reside.
Unlike Álfheimr, the home of light elves ruled by the Vanir god Freyr, which is bright and ethereal, Svartalfheim is characterized by its shadowy landscapes and hidden depths.
Svartalfheim plays a crucial role in Norse mythology. It is depicted as a dark, labyrinthine domain located deep beneath the earth’s surface – almost like another kind of Underworld besides Hel’s realm.
This realm represents not only a physical location but also symbolizes the darker aspects of existence and nature. The dark elves, or Dökkálfar, who inhabit this realm are often associated with craftsmanship, magic, and sometimes malevolence.
The stark contrast between Álfheimr and Svartalfheim highlights the duality present in Norse beliefs. Álfheimr, filled with light and beauty, represents purity and goodness.
On the other hand, Svartalfheim embodies darkness and complexity. Despite their differences, these realms are interconnected.
While Álfheimr is ruled by Freyr—a god associated with prosperity and sunlight—Svartalfheim does not have a singular ruler but is influenced by various powerful inhabitants known for their skills in forging and enchantment.
Geography greatly impacts how dark elves are perceived in Norse mythology. The underground nature of Svartalfheim suggests secrecy, hidden knowledge, and a connection to the earth’s raw elements. This geographical context shapes their characteristics:
Understanding Svartalfheim helps us appreciate the complex relationship between light and darkness that defines Norse cosmology.
The realm’s hidden depths reflect the Dökkálfar’s own elusive nature, making them essential in exploring themes of balance within Norse Scandinavian Viking culture.
Dark elves, or Dökkálfar, present a striking contrast to their lighter counterparts, the Ljósálfar. Their physical appearance is often described as being darker than pitch, with a dusky complexion that embodies the very essence of shadow.
This vivid description conjures images of beings shrouded in mystery and darkness, living far from the reach of sunlight.
The Dökkálfar are renowned for their magical prowess. They possess abilities that make them formidable entities within Norse mythology:
In Norse mythology, Dökkálfar occupy dual roles:
This duality underscores their complex nature, embodying both the potential for great creation and significant destruction. Their contributions to the mythological world were indispensable, yet their presence often invoked a sense of foreboding.
The intricate balance between light and dark themes in Norse mythology finds a poignant expression in the existence and abilities of the Dökkálfar. This balance allows us to appreciate not just their magical abilities but also their crucial role in the broader tapestry of Viking lore.
It may be a rather surprising and perhaps fascinating possibility to think that the concept of dark and light elves were initially the same as the Vanir Gods and that the good and evil aspects assigned to them both is a rather late development (Hilda Davidson, 1988, p. 173).
Norse mythology is full of stories that explore the balance between light and darkness, good and evil. Some of them may be older, others may be much more recent and more influenced by contact with Christianity.
One of the most striking examples of this duality can be seen in the contrasting figures of the Dökkálfar (dark elves) and Ljósálfar (light elves).
The myths often delve into how light and dark forces interact with each other:
This comparison not only highlights physical differences but also moral ones. The Dökkálfar’s realm underlines their connection to darkness and the unknown, reflecting humanity’s eternal struggle with inner demons and external threats.
The portrayal of Dökkálfar raises intriguing questions about morality. Unlike the clear-cut distinctions often seen in modern tales of good versus evil:
The interplay between light and darkness in these myths reflects deeper philosophical inquiries into human nature:
By examining these themes, you gain insight into how ancient Norse beliefs shaped understandings of morality, existence, and the universe itself. This understanding enriches your appreciation for Viking culture’s intricate mythological landscape.
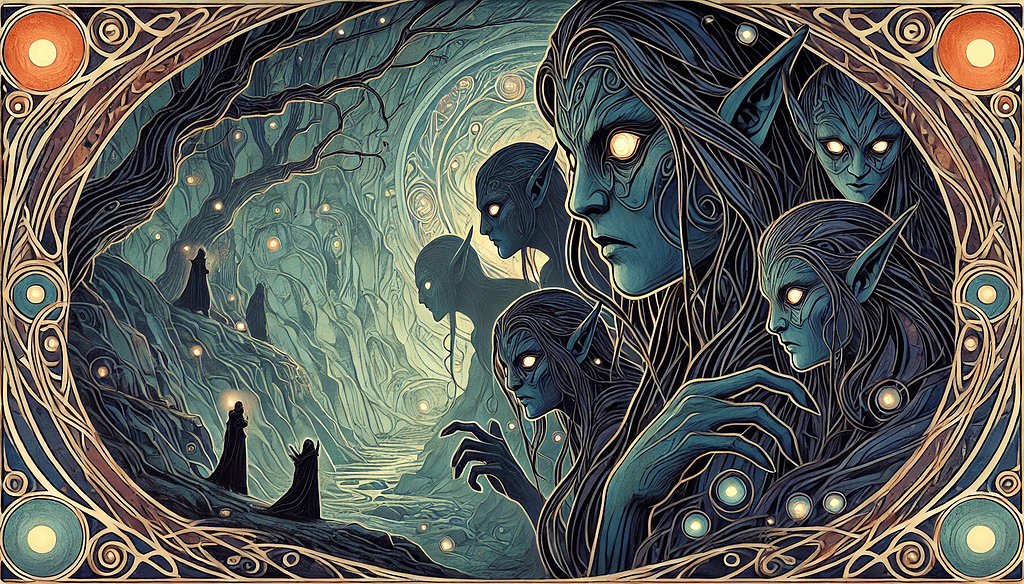
Modern fantasy owes a significant debt to Norse mythology, especially in its depiction of dark elves. The evolution of these enigmatic beings in literature and media has been nothing short of fascinating.
J.R.R. Tolkien’s work serves as a cornerstone for understanding this transformation. In his seminal series, The Lord of the Rings, Tolkien introduced a diverse range of elves, including those with darker traits.
Though not explicitly labeled as Dökkálfar, the influence of dark elves in Norse mythology can be seen in characters like the sinister Orcs, who were once elves corrupted by evil.
Tolkien’s influence on pop culture is undeniable; his portrayal has trickled down into countless modern narratives.
In the realm of modern literature, games like Dungeons & Dragons have further popularized dark elf characters.
Known as Drow, these black-skinned elves possess a rich lore that intertwines with themes of treachery and an underworld existence, reminiscent of their Norse counterparts.
Players often encounter Drow as formidable adversaries or complex allies, adding layers to their campaigns.
Video games have also embraced dark elves with enthusiasm:
Elves in modern culture frequently straddle the line between light and darkness, echoing their ancient roots while evolving to fit contemporary narratives.
Whether depicted as noble or nefarious, their enduring presence highlights our fascination with these mystical beings.
The transition from ancient myths to modern storytelling showcases how Tolkien’s influence on pop culture has reshaped our understanding of dark elves, blending traditional elements with innovative twists to keep these legends alive and relevant.
Dark elves, or Dökkálfar, often bear a reputation for embodying malevolence. Yet, this perspective oversimplifies their role in Norse mythology. These entities are not merely evil caricatures; they represent the nuanced interplay between light and darkness.
While many narratives depict them as malevolent, their characteristics vary widely across different sources.
Dark elves were known for their association with the earth and darkness, and their actions often reflected these attributes. They could be both creators and destroyers, suggesting that their moral alignment is more complex than simply being ‘evil.’
Svartalfheim is one of the nine worlds in Norse cosmology and serves as the home of the dark elves. This realm is depicted as being subterranean, filled with labyrinthine tunnels and caverns where these dusky elves dwell.
The dark complexion of the Dökkálfar mirrors the shadows of their homeland. Svartalfheim’s geography significantly influences how these beings are perceived. Their mystical abode is shrouded in mystery and darkness, contributing to their enigmatic nature.
For those exploring beliefs about elves, understanding Svartalfheim provides a deeper insight into why dark elves embody certain attributes.
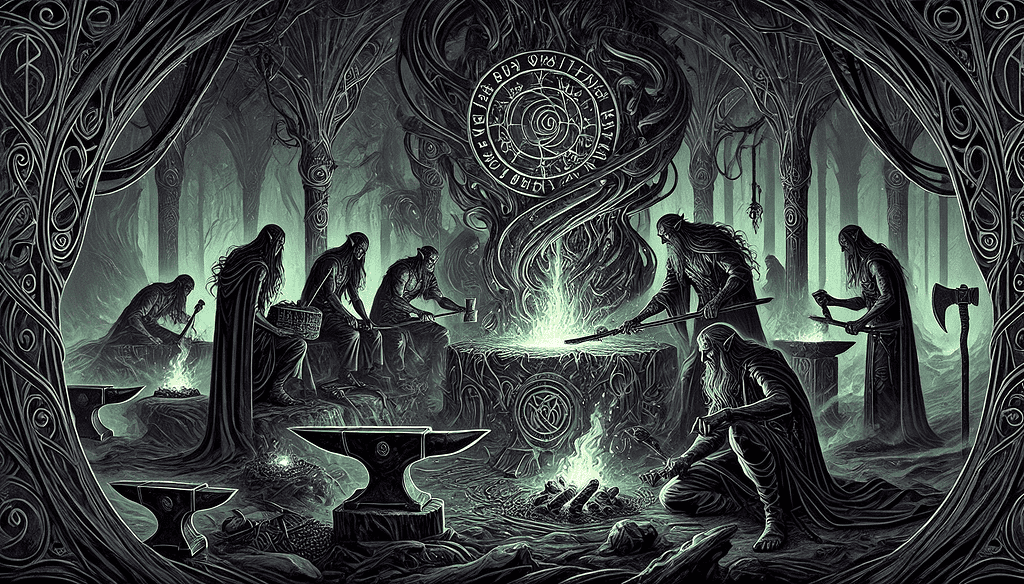
A common question arises: Are dark elves just another term for dwarves? The confusion stems from overlapping descriptions in various texts.
Both groups are associated with underground realms, craftsmanship, and magical abilities. However, distinctions exist.
Elves were known to be more ethereal compared to the sturdier, more physically grounded dwarves. Snorri Sturluson’s Prose Edda often blurs these lines but generally treats them as separate entities.
Understanding these differences enriches our comprehension of Norse mythology’s intricate tapestry and clarifies why both groups hold unique places within it.
Exploring these questions provides a clearer picture of the enigmatic Dökkálfar and their place in Norse mythos.
Understanding the Dökkálfar extends beyond mere mythology. For modern pagans and enthusiasts, these enigmatic beings symbolize a profound connection to ancient beliefs and the intricate balance of light and darkness.
By delving into the lore of dark elves, you gain insight into the dualistic nature of Norse mythology—a reminder that both light and darkness are essential components of existence. This understanding enhances your appreciation for the complexity within these ancient stories.
“In every shadow, there is light; in every light, there is shadow.”
Exploring the importance of understanding Dökkálfar enriches your connection to Viking heritage and provides a nuanced perspective on good and evil. Whether through handcrafted jewelry or personal study, embracing this mystique allows you to keep the spirit of Norse mythology alive today.
References and literature for further study:
Lecouteux, Claude. (2016). Encyclopedia of Norse and Germanic Folklore, Mythology, and Magic. United States: Inner Traditions/Bear.
Davidson, D. H. E., Davidson, H. E. (2002). The Lost Beliefs of Northern Europe. United Kingdom: Taylor & Francis.
Davidson, H. R. E. (1988). Myths and Symbols in Pagan Europe: Early Scandinavian and Celtic Religions. United Kingdom: Manchester University Press.